Last Updated on December 28, 2025 by DarkNet
The Dark Web is a concealed segment of the internet that can be accessed only through specialized software such as Tor. In 2026, it remains an increasingly influential part of the digital landscape. Often portrayed as the internet’s shadowy underworld, the Dark Web hosts a wide range of marketplaces that offer products and services ranging from privacy enhancing tools and digital currencies to activities that are ethically questionable or outright illegal. As digital surveillance continues to expand and public concern about online privacy grows, understanding how these anonymous marketplaces function has become essential not only for cybersecurity professionals and researchers but also for anyone interested in how digital anonymity is shaping the future of commerce and personal privacy.
This article presents in depth overviews of the top 11 Dark Web marketplaces shaping the hidden internet landscape in 2026. It explores their defining features, common use cases that include both legitimate and illicit activity, and the significant risks associated with engaging with these platforms. Whether you are a security professional seeking to stay ahead of emerging digital threats, a journalist searching for secure communication methods in restrictive environments, or a technology enthusiast intrigued by the lesser known layers of the internet, this guide offers critical insight into the realities of Dark Web commerce in 2026.
How Dark-Web Marketplaces Operate in 2026
Dark-web marketplaces operate through encrypted networks, primarily utilizing anonymity-enhancing technologies such as Tor (The Onion Router) and I2P (Invisible Internet Project). These technologies obscure users’ identities and locations by routing their internet traffic through multiple volunteer-operated servers worldwide, making it extremely difficult to trace activities back to individuals. Tor remains the most prevalent method due to its ease of use and robust anonymity features, but the popularity of I2P is steadily growing due to its increased resistance to surveillance and censorship.
Transactions within these marketplaces typically leverage cryptocurrencies—most commonly Monero, Bitcoin, and privacy-centric digital currencies developed specifically to enhance transaction anonymity. Monero, in particular, has become the preferred cryptocurrency on the dark web in 2026 due to its advanced privacy mechanisms, which obscure transaction histories and wallet balances from public view.
Significant technological innovations and trends have reshaped dark-web marketplaces over recent years. In 2026, many platforms have adopted decentralized architectures, reducing single points of failure that previously made them vulnerable to law enforcement takedowns. Additionally, artificial intelligence tools are increasingly being used to manage transactions, vet vendors, and enhance user security—automating dispute resolution, escrow processes, and reputation systems to build trust and streamline operations.
Another notable trend is the rise of encrypted peer-to-peer (P2P) messaging systems integrated directly within marketplaces, providing secure communication channels between buyers and sellers. The integration of blockchain-based smart contracts is also becoming widespread, automating secure transactions and reducing the likelihood of fraud.
Overall, dark-web marketplaces in 2026 are more sophisticated, secure, and resilient than ever before, evolving rapidly in response to both technological advancements and intensified scrutiny from global law enforcement agencies.
Criteria for Choosing the Best Dark-Web Marketplaces
Selecting the right dark-web marketplace in 2026 involves careful consideration of several critical factors. For users prioritizing privacy, security, and reliability, evaluating these key criteria is essential:
1. Security
Security is the cornerstone of any dark-web marketplace. Users must look for platforms employing robust encryption protocols, secure escrow services, and advanced anti-phishing measures. Additional layers, such as two-factor authentication (2FA), encrypted PGP messaging, and built-in wallet security, significantly enhance protection against theft and hacking.
2. Anonymity
Maintaining anonymity is paramount. Ideal marketplaces support anonymous browsing through networks like Tor and I2P, utilize privacy-focused cryptocurrencies such as Monero, and implement measures to prevent tracking and transaction tracing. Platforms that provide clear guidelines for maintaining operational security (OpSec) and offer built-in tools for data obfuscation are especially favored.
3. Reputation
Marketplace reputation reflects trustworthiness and reliability. Experienced users typically prefer marketplaces with robust vendor rating systems, detailed feedback options, and transparent dispute resolution processes. Platforms known for consistently resolving issues and eliminating fraudulent vendors quickly gain credibility and user loyalty.
4. Usability
An intuitive, user-friendly interface is crucial, especially given the complex nature of dark-web interactions. Users favor marketplaces with straightforward navigation, efficient search functions, and clear product categorizations. The ability to seamlessly communicate with vendors via secure messaging systems also greatly improves overall user experience.
5. Range of Available Products
Finally, product variety significantly influences marketplace choice. The best marketplaces in 2026 cater to diverse needs, offering a broad spectrum of products ranging from privacy-enhancing software, digital documents, and cryptocurrency exchanges to more sensitive or controversial goods. Marketplaces that maintain strict moderation policies—banning excessively harmful or exploitative products—also gain popularity among more ethically minded users.
By carefully assessing these critical criteria—security, anonymity, reputation, usability, and product range—users can confidently select marketplaces that align with their needs while minimizing potential risks associated with dark-web interactions.
Comparative Snapshot of Key Platforms
| Marketplace | Focus / Region | Access | Currencies | Payments / Escrow | Security & Privacy (publicly described) | Notables | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BlackOps Market | General-purpose, global (English) | Tor | XMR-only (self-reported) | Escrow, multisig emphasis (self-reported) | PGP, 2FA mandatory (self-reported) | Emerging platform since late 2024; limited independent verification, no well-sourced public incident reports. | Active |
| Catharsis Market | General-purpose, drugs-focused (English) | Tor | BTC, XMR, LTC (self-reported) | Escrow (self-reported) | PGP, 2FA; vendor migration tools (self-reported) | Active community discussion; no well-sourced public incident reports in 2024–2025. | Active |
| Abacus Market | Broad, English‑language, global | Tor (had a clearnet status page/mirror) | BTC, XMR | Standard escrow | PGP messaging, 2FA, anti‑phishing warnings, vendor verification (reported by TI firms) | Went offline in July 2025; multiple TI and news outlets assess a likely exit scam following withdrawal issues. | Active |
| Nexus Market | General‑purpose, global (English) | Tor | BTC, XMR (self‑reported) | Escrow (self‑reported) | PGP, 2FA (self‑reported) | No major, well‑sourced public incident reports in 2024–2025; coverage in mainstream TI roundups is limited. | Active |
| TorZon Market | Broad catalog (drugs, fraud, digital) | Tor | BTC, XMR | Escrow; PGP‑verified review imports; premium tiers; raffle feature (per TI) | PGP messaging, 2FA; rotating mirrors (TI reporting) | Drew migrating vendors/users after the Archetyp takedown in June 2025. | Active |
| WTN / WeTheNorth Market | Canada‑focused, bilingual (EN/FR); drugs, fraud, digital | Tor (with a clearnet front noted by TI) | BTC, XMR | Escrow; separate cards autoshop; balances shown in CAD for users (per TI) | PGP; 2FA; forum + marketplace | Consistently listed in 2025 TI roundups of active markets with a regional tilt. | Active (regional). |
| Kerberos Market | General (drugs, digital goods, stolen data); emphasis on UX/security | Tor | BTC, XMR | Escrow (typical) | PGP available; 2FA commonly required (varies by source) | Identified by Europol IOCTA 2024 as an emerging market; launched in 2022 and accepts BTC/Monero. | Active |
| DarkMatter Market | Mixed catalog; Monero‑centric | Tor | XMR‑only (Monero) | Walletless ordering; XMR multisig escrow (per TI/trackers) | PGP; 2FA (self‑reported by trackers) | Brand sees persistent phishing/impersonation attempts; one scam subreddit promoting phishing was banned in July 2025. | Active (XMR‑only model). |
| Apocalypse Market | General (drugs, fraud, digital) | Tor (sometimes I2P) | BTC, XMR (self‑reported) | Multisig / time‑lock escrow (self‑reported) | PGP, 2FA (self‑reported) | Credibility dented by a 2023 admin IP leak incident widely discussed in OSINT write‑ups; status fluctuated thereafter. | Active |
| Flugsvamp 4.0 | Sweden‑focused (successor to FS3) | Tor | — | Standard escrow | — | Launched Nov 2, 2021; never matched FS3’s popularity | Active |
| Ares Market | Broad (drugs, counterfeits, hacking/fraud) | Tor | BTC, XMR | Walletless (direct‑pay to order escrow); FE for vetted vendors | PGP required for vendors; 2FA (per market FAQ) | Profiled by TI researchers in 2024; tracker pages document walletless flow and coin support. | Active |
Catharsis Market
Catharsis Market is described by community trackers as an active, general-purpose darknet marketplace with a strong focus on narcotics and other illicit goods. It operates on the Tor network and, according to self-reported claims, supports Bitcoin, Monero, and Litecoin. Users frequently highlight its emphasis on continuity with older markets by allowing vendors to migrate reputations and listings—an increasingly common feature among newer DNMs.
Key Goods and Services Offered
Public discussions portray Catharsis Market as primarily centered on drug-related listings while still hosting the broad mix of categories typical for darknet platforms. Vendor offerings reportedly include:
-
Pharmaceuticals and controlled substances: cannabis, stimulants, psychedelics, and other drug categories, depending on vendor policy.
-
Digital or “gray-zone” items: privacy tools, software utilities, and miscellaneous digital services, similar to patterns seen on other DNMs.
-
Fraud-related goods: prepaid accounts or digital financial items, varying by vendor and not consistently documented.
Trackers note that, like several modern markets, Catharsis claims to prohibit highly harmful or reputationally damaging categories (e.g., explicit abuse material, certain forms of violence-related content). Such bans can influence users’ trust perceptions but do not mitigate the inherent risks of illicit-market environments.
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
-
Vendor Migration & Reputation Transfer: Catharsis differentiates itself by advertising tools that let vendors import past ratings, helping new sellers establish credibility more quickly.
-
Escrow & Dispute Processes: As with most contemporary DNMs, a standard escrow system is described, with moderators handling disputes to reduce routine scams.
-
Multi-currency Support: Self-reported acceptance of BTC, XMR, and LTC aligns with the broader trend of supporting privacy-centric coins like Monero.
Weaknesses
-
Market Volatility: Catharsis operates in the same unstable ecosystem affecting all DNMs—susceptible to DDoS attacks, phishing, impersonation, abrupt closures, and potential exit-scams.
-
Limited Verifiable Information: Because the market is a hidden service, public, well-sourced documentation is scarce; most insights come from informal community trackers that can be outdated or inconsistent.
Security and Anonymity Features
Open-source summaries about Catharsis—and modern darknet markets in general—suggest several broad patterns:
-
Tor-based access and encrypted buyer-vendor communication, typically relying on PGP workflows.
-
Optional or recommended account protections, such as 2FA for vendors and anti-phishing checks encouraged by community guides.
-
Escrow-based payments with mediated dispute resolution, intended to reduce opportunistic fraud.
-
Support for privacy-focused cryptocurrencies (e.g., Monero), reflecting ecosystem-wide preferences for enhanced transactional anonymity.
Overview
In public sources, Catharsis Market is portrayed as a contemporary darknet marketplace that mirrors the established feature set of second-generation DNMs: escrow, vendor ratings, moderation, PGP-based security, and privacy-coin support. While these elements may improve user confidence relative to older markets, they do not eliminate the defining risks of the environment—platform instability, phishing campaigns, information gaps, and ongoing law-enforcement pressure remain persistent realities.
BlackOps Market
BlackOps Market is described in community sources as a privacy-first, general-purpose dark-web marketplace that emerged in late 2024 and continued gaining visibility into 2025. Trackers characterize it as a newer, security-centric platform emphasizing Monero-only transactions, hardened account controls, and a “PGP + escrow + multisig-encouraged” model aligned with more privacy-oriented DNMs. Independent verification remains limited due to the market’s relatively recent appearance.
Key Goods and Services Offered
Like comparable markets, BlackOps is reported to host a range of vendor-supplied listings spanning both “gray-area” privacy tools and clearly illicit categories:
-
Privacy-focused digital goods: encrypted-communication apps, secure cloud/storage solutions, VPN accounts, and similar software commonly traded across DNMs.
-
Cryptocurrency/financial items: prepaid cards, exchange credits, and various underground financial services (availability varies by vendor).
-
Digital and counterfeit products: forged or templated documents, digital IDs, and related materials offered by independent sellers.
-
Pharmaceuticals and controlled substances: cannabis, psychedelics, and select stimulants, subject to internal moderation and vendor compliance rules at the time.
Trackers also note that BlackOps, like many modern DNMs, claims to prohibit the most high-risk and exploitative categories (e.g., sexual-abuse material, weapons, and certain ultra-lethal substances), though such policies vary and do not eliminate legal or operational risk.
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
-
Privacy-first design: BlackOps’s Monero-only model appeals to users seeking maximum on-chain obfuscation and reflects a growing trend toward privacy coins within DNMs.
-
Security Controls: Sources describe enforced PGP usage, mandatory 2FA, and encrypted messaging, mirroring best practices among higher-security marketplaces.
-
Escrow & Multisig Orientation: The platform promotes escrow workflows and multisig support, aiming to reduce fraud and establish trust for high-value transactions.
-
Vendor Screening: Emerging reputation and feedback systems help distinguish more established vendors, though the ecosystem is still developing.
Weaknesses
-
New-market Trust Gap: As a relatively recent marketplace, BlackOps lacks the long-term reputation and historical uptime associated with older DNMs, making reliability harder to gauge.
-
Ecosystem Volatility: Like all DNMs, BlackOps operates amid constant phishing, DDoS pressure, takedown attempts, and exit-scam risk. The 2024–2025 period saw multiple international operations targeting major markets, impacting user trust across the ecosystem.
-
Limited Independent Documentation: Much of what is known comes from community trackers and aggregator sites, which can be incomplete or outdated.
Security and Anonymity Features
Open-source descriptions of BlackOps—and modern security-oriented DNMs in general—highlight several core elements:
-
Tor-based access with enforced PGP communication and encrypted internal messaging.
-
Mandatory 2FA for vendors and strongly recommended for buyers, paired with anti-phishing hygiene emphasized by trackers.
-
Escrow with structured dispute resolution to reduce basic fraud schemes.
-
Monero-only payments, reflecting sector-wide preferences for minimizing blockchain traceability and avoiding Bitcoin-based surveillance.
BlackOps Market is portrayed in open sources as a modern, privacy-driven dark-web marketplace built around Monero-only transactions, strict account-security practices, and familiar trust mechanisms (escrow, feedback, vendor screening). While its emphasis on privacy and PGP-based workflows aligns with current DNM trends, core risks remain: volatility, phishing, potential exit events, and law-enforcement exposure continue to define the ecosystem, and specific conditions can shift rapidly.
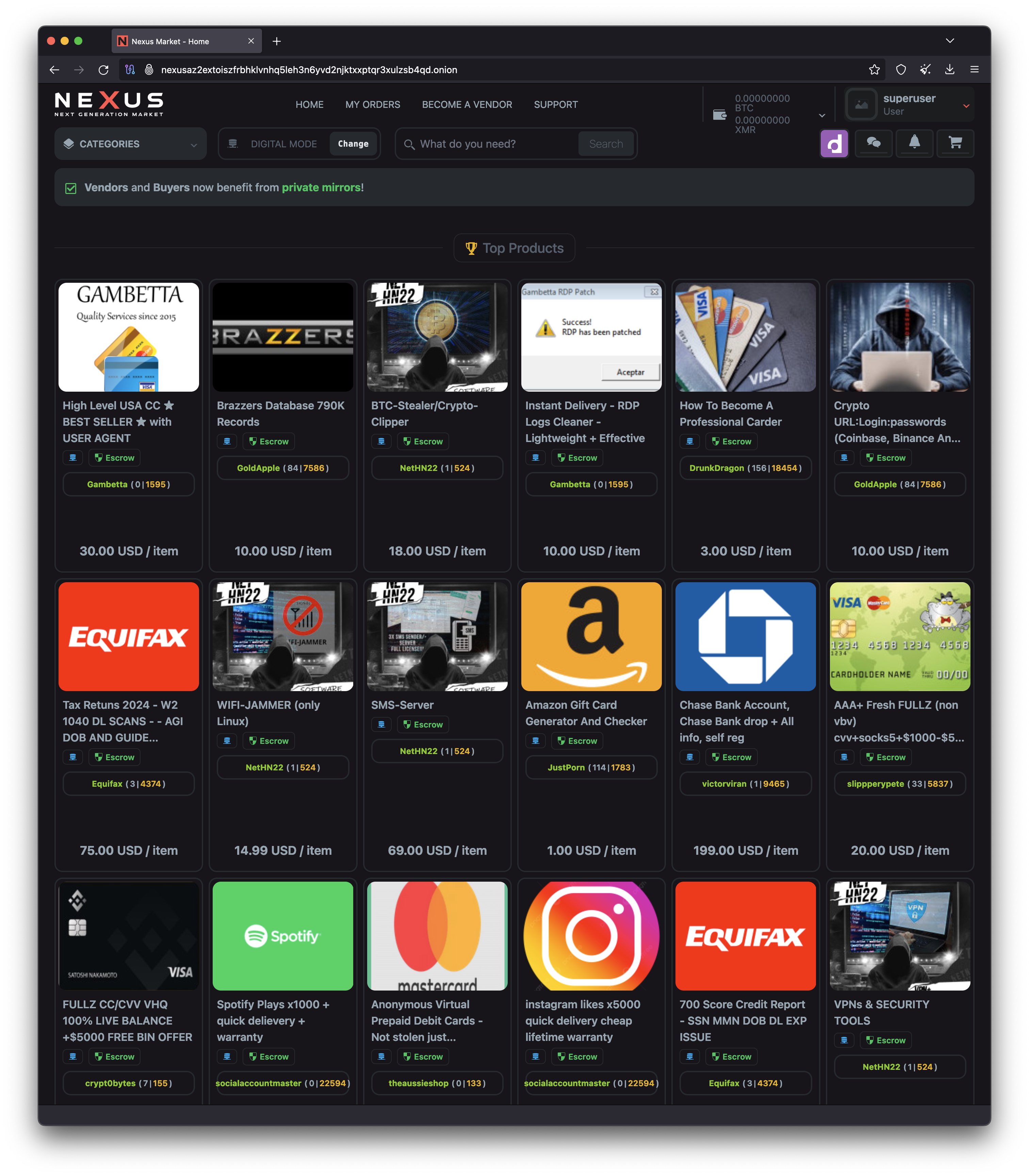
Nexus Market
Nexus Market is widely described as a second‑generation, general‑purpose dark‑web marketplace that gained traction through 2024–2025. Community trackers place its launch in late 2023 and note a focus on stability, moderation, and a familiar “escrow + vendor‑reputation” model typical of modern DNMs. Public sources also indicate support for both Bitcoin and privacy‑centric coins, aligning with broader ecosystem trends.
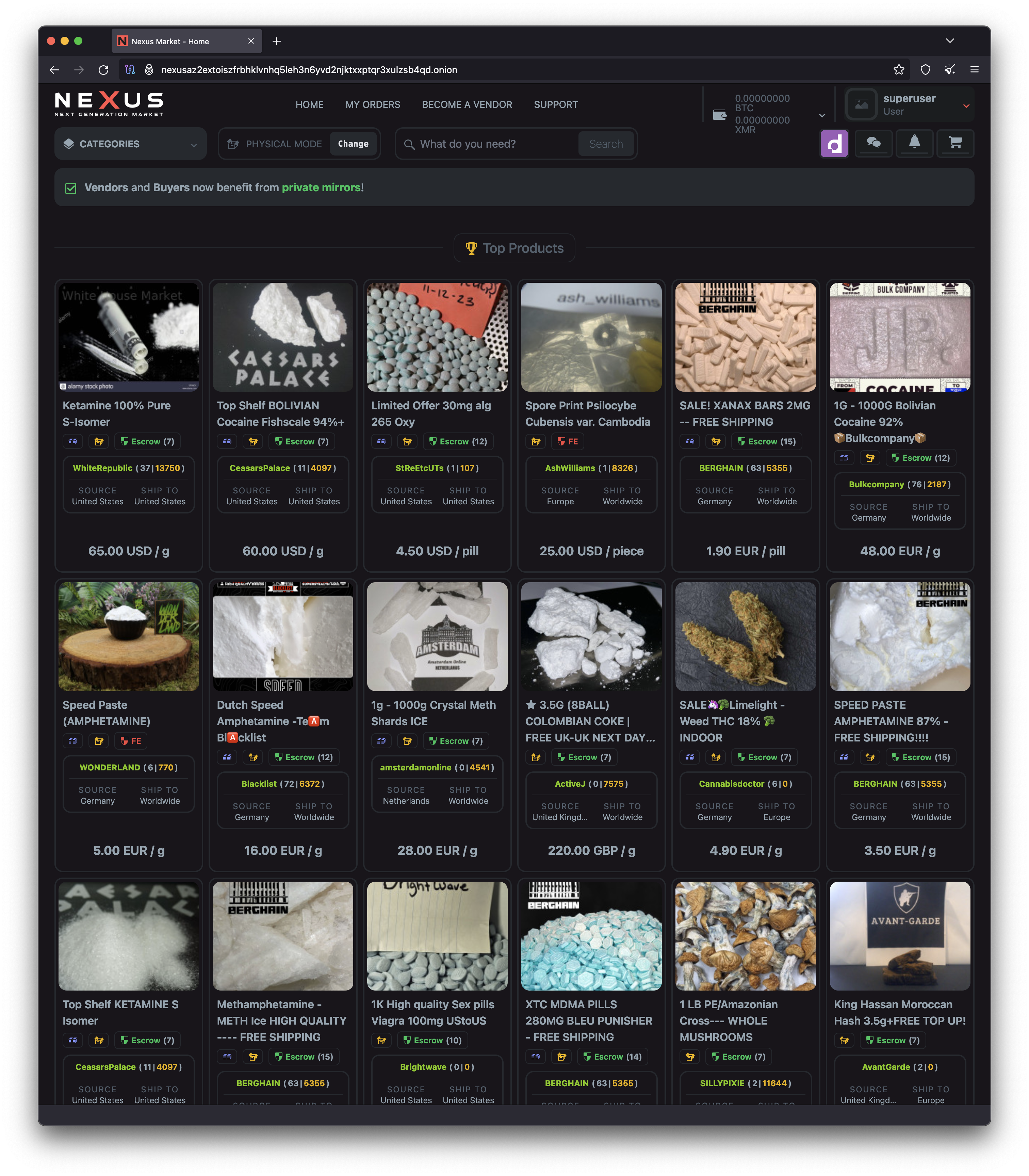
Key Goods and Services Offered
As with comparable markets, Nexus’s listings reportedly span both “gray” privacy tools and clearly illicit categories offered by independent vendors:
-
Privacy‑oriented digital goods: encrypted communications utilities, VPN subscriptions, secure storage, and related software. (General DNM patterns.) Wikipedia
-
Cryptocurrency/financial services: exchange vouchers, prepaid cards, and other financial accounts circulating in underground economies (descriptions vary by tracker).
-
Digital and counterfeit items: forged IDs, licenses, and similar documents (vendor‑provided).
-
Pharmaceuticals and controlled substances: from cannabis and psychedelics to select stimulants, subject to internal rules. (Policy details differ by market and over time.)
Trackers also note that Nexus, like many peers, explicitly bans highly dangerous or exploitative categories (e.g., weapons and sexual‑abuse material; some sources also mention fentanyl), which can improve standing among users without eliminating legal risk.
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
-
Security & Account Controls: Community write‑ups mention mandatory PGP use and two‑factor authentication for vendors, with built‑in encrypted messaging—features consistent with best practices across DNMs.
-
Escrow & Disputes: Standard escrow and formalized dispute workflows aim to reduce scams and increase buyer confidence—again mirroring the broader marketplace model. Vaiyo
-
Vendor Management: Reported verification steps and reputation/feedback systems help filter low‑quality sellers and surface reliable vendors over time. Find Darknet Markets working Links
Weaknesses
-
Ecosystem Volatility: Even well‑run markets operate amid persistent DDoS, phishing, takedowns, and exit‑scam risk; 2024–2025 saw ongoing multi‑country operations against major DNMs, keeping trust fragile.
-
Information Asymmetry: Because Nexus is a hidden service, authoritative, up‑to‑date documentation is limited; much of what’s known comes from community trackers that can lag reality.
Security and Anonymity Features
Open‑source descriptions of Nexus—and of mature DNMs generally—highlight:
-
Access over anonymity networks and encrypted vendor/buyer messaging, often with PGP baked into workflows. Wikipedia
-
Account‑level protections (e.g., 2FA for vendors; 2FA recommended for buyers), plus anti‑phishing hygiene promoted by trackers.
-
Escrow with moderated disputes to limit straightforward “take‑the‑money” fraud.
-
Cryptocurrency support that includes privacy‑focused options (e.g., Monero) alongside Bitcoin, reflecting sector‑wide preferences for obfuscation.
Nexus Market is portrayed in open sources as a modern, general‑purpose DNM that blends familiar trust mechanisms (escrow, feedback, vendor screening) with stronger account hygiene (PGP/2FA) and privacy‑coin support. Those strengths don’t remove core risks: volatility, phishing, and law‑enforcement exposure remain defining features of the ecosystem, and specifics change frequently.
TorZon Market
TorZon Market is a large, general‑purpose dark‑web marketplace that’s frequently cited in 2024–2025 roundups. Public trackers place its launch around September 2022. It operates on Tor and, by 2025, is commonly reported as hosting tens of thousands of active listings. To make seller reputations more portable, TorZon supports imported, PGP‑signed reviews, and it accepts both Bitcoin and Monero. The platform also advertises user‑engagement features such as a raffle and paid account upgrades for expanded functionality.

Key Goods and Services Offered
Inventory varies by independent vendors but generally includes:
-
Narcotics and pharmaceuticals
-
Fraud/financial services and data (e.g., cards, accounts)
-
Hacking tools and services (software, exploits, “kits”)
-
Counterfeit documents (IDs, passports, licenses)
-
Digital goods (accounts, VPN/cloud services, guides/manuals)
Note on moderation policy: Some sources say TorZon bans overtly violent/exploitative categories (e.g., weapons, “hitman” services, child‑abuse content). Others have observed a weapons section at various times. Rules and their enforcement appear to be fluid and time‑dependent.
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
-
Seller reputation transparency: Importing reviews with PGP proofs helps vendors carry reputation between markets and reduces information asymmetry for buyers.
-
Baseline security model: Escrow, formalized dispute resolution, and built‑in PGP messaging; rotating onion addresses to counter phishing/monitoring.
-
Engagement mechanics: Raffles and account‑tier upgrades that encourage user retention (without mitigating legal risk).
Weaknesses
-
Availability and resilience: Like most DNMs, TorZon faces DDoS and phishing pressure, prompting mirrors, CAPTCHAs, and frequent link rotation.
-
Law‑enforcement pressure and exit risk: The sector remains unstable due to multi‑agency operations and occasional market “disappearances,” which shape user migration and confidence across the ecosystem.
-
Incomplete open‑source visibility: As a hidden service, authoritative, up‑to‑date details are scarce; much of what’s known comes from community trackers and can lag reality.
Security and Anonymity Features
-
Tor‑only access with active mirror rotation
-
PGP‑centric workflows: vendor verification and encrypted buyer–seller messaging; support for PGP‑signed review imports
-
Escrow and moderated disputes with a reputation/feedback system
-
Cryptocurrency support: BTC/XMR as primary settlement options
-
Edge protections: stricter onboarding steps, CAPTCHAs, and anti‑abuse checks
TorZon Market fits the “second‑generation” DNM pattern: portable, PGP‑verified reputations; standard trust/safety mechanisms (escrow, dispute handling, encrypted comms); and privacy‑oriented payments (Monero alongside Bitcoin). Those strengths do not remove core risks: phishing/DDoS, infrastructure volatility, and sustained law‑enforcement attention all materially affect access and trust.
WTN Market (WeTheNorth)
WTN Market (WeTheNorth) is a Canada‑focused dark‑web marketplace that emerged after the shutdown of CanadianHQ and has leaned into a regional identity (English/French support, CAD‑oriented account views). Public threat‑intel places its launch in 2021 and notes a design and workflow similar to mainstream DNMs. As of April 22, 2025, open‑source monitoring counted 9,000+ listings across drugs, fraud, counterfeit documents, malware, and “how‑to” guides. The site emphasizes on‑platform interactions and cryptocurrency settlement.
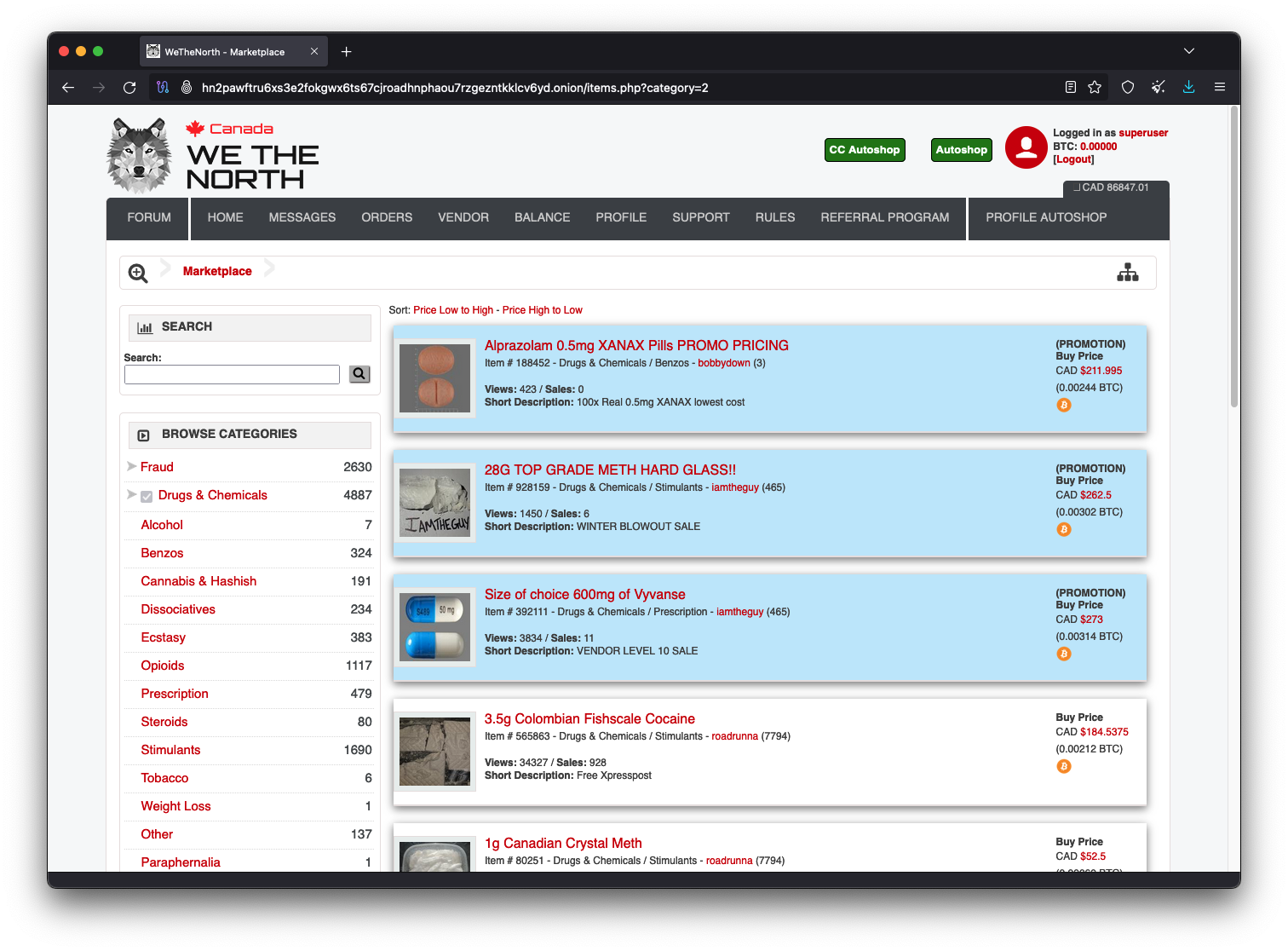
Catalog and Moderation
-
Dominant categories: Drugs & Chemicals, Fraud, Guides & Tutorials, plus Software & Malware and Security & Hosting. Listing volumes fluctuate, but drugs typically lead, followed by fraud and guides.
-
Rules and exclusions: Sources describe explicit bans on weapons, terrorism‑related content, doxxing, and third‑party contact info (e.g., Telegram in listings), with an emphasis on keeping buyer–seller communication inside the platform.
What It Does Well
-
Regional positioning: Aims to serve Canadian buyers/sellers with bilingual support and an interface that surfaces balances and activity in BTC and CAD, making the UI feel familiar to its audience.
-
Trust and marketplace mechanics: Standard escrow and reputation/feedback systems, an integrated forum, and a structured vendor program are intended to reduce scams and centralize dispute handling. For some digital goods (e.g., cards), an autoshop enables instant fulfillment.
-
Account‑level safeguards (per early research): Prior reporting notes 2FA for vendors, unique signup tokens to protect accounts, non‑refundable vendor fees to discourage churn, and 24/7 support—signals of an attempt to professionalize operations.
Trade‑offs and Limitations
-
Escrow coverage isn’t universal: Autoshop‑style, instant‑delivery listings can bypass traditional escrow workflows, which may improve speed but weakens buyer protections relative to fully moderated transactions.
-
Narrow geographic focus: The Canada‑centric model builds community but can limit product breadth compared to global markets; inventory and enforcement vary over time.
-
Law‑enforcement pressure remains a constant: WTN arose in the wake of CanadianHQ’s takedown and exists in a space characterized by DDoS, phishing, seizures, and occasional market exits; trust can shift quickly.
Security & Privacy Controls (as described in open sources)
-
Access & comms: Tor access, on‑platform messaging, and restrictions on external contact details to contain interactions.
-
Account security: Reports of two‑factor authentication (vendors) and unique account tokens aim to reduce compromise; bilingual customer support is cited in early research.
-
Transaction model: Cryptocurrency‑based settlement (UI shows BTC/CAD), standard escrow and dispute paths; forum and mirrors to sustain availability during attacks.
WTN Market positions itself as a localized, bilingual marketplace with familiar DNM trust mechanisms (escrow, ratings, forum) and a UI tailored to Canadian users. Those choices do not negate core ecosystem risks—availability volatility, phishing/DDoS, and persistent enforcement pressure—so public details can change quickly.
Kerberos Market
Kerberos Market is commonly cited by law‑enforcement and OSINT trackers as a newer, general‑purpose marketplace. Europol’s 2024 IOCTA notes Kerberos as a prominent “emerging” market, launched in 2022 with a focus on end‑user experience and security, a wide product mix (from drugs to digital items and stolen data), and Bitcoin/Monero support. Self‑described landing pages also advertise additional coins and platform hardening features, but these claims are not independently verified.
Catalog & Positioning
Vendor listings (as described in public sources) span typical DNM categories:
-
Drugs & pharmaceuticals,
-
Digital items and stolen data,
-
Counterfeit/identity documents, and other vendor‑driven offerings.
These categories align with Europol’s description of Kerberos’s product scope and third‑party trackers’ summaries.
What It Does Well (as reported)
-
Security‑forward feature set: Public pages and trackers describe PGP‑based messaging, 2FA options (PGP or TOTP), reputation/feedback, and multisig/escrow flows intended to reduce straightforward fraud. Some sources also mention a vendor bond model for new sellers.
-
Payments and privacy: Europol lists BTC/XMR support; self‑described pages add ETH/LTC among supported options (caveat: platform‑provided claims). The mix mirrors a broader ecosystem drift toward privacy‑coins.
-
Access model: Operates over Tor; some self‑described pages additionally claim I2P access. Treat I2P availability as unconfirmed marketing unless corroborated.
Trade‑offs & Ongoing Risks
-
Ecosystem volatility: The DNM space remains unstable—markets face seizures, exit‑scams, and migrations. Chainalysis’s 2025 review highlights recent takedowns and an exit‑scam at a major peer, plus a trend toward XMR‑only operations to avoid BTC traceability. Such dynamics affect user confidence across markets, Kerberos included.
-
Availability pressure: DNMs frequently battle DDoS and phishing; mirror rotation and anti‑phishing measures are standard countermeasures but don’t eliminate downtime or impersonation risk. (General DNM risk; platform pages emphasize mitigations, but uptime is inherently fluid.)
-
Self‑reported features vs. independent validation: Much of what’s known about Kerberos’s operational details (e.g., “Cataclysm Protocol,” specific fee policies, or coin menus) comes from platform‑controlled or community pages; treat these as indicative, not definitive.
Security & Anonymity Model (as described publicly)
-
Account & comms: PGP for vendor/buyer messages; 2FA available (PGP or TOTP).
-
Transaction layer: Escrow (often with multisig), disputes, and a reputation system; some sources mention vendor bonds for new sellers.
-
Payment options: At minimum BTC/XMR per Europol; platform pages add ETH/LTC.
Kerberos Market positions itself as a security‑centric, general‑purpose DNM: familiar trust mechanics (escrow, feedback), crypto options oriented toward privacy, and PGP‑first workflows. Those strengths don’t remove structural risks—law‑enforcement pressure, phishing/DDoS, exit‑scams, and shifting mirrors remain defining features of the ecosystem—so details can change quickly.
Abacus Market
Abacus Market has emerged as one of the most reputable and widely used dark-web marketplaces in 2025. Founded in early 2023, shortly after major law enforcement operations shut down several competing platforms, Abacus quickly filled the void by prioritizing reliability, advanced security, and user anonymity.
Key Goods and Services Offered
Abacus Market offers a diverse range of products, appealing to a broad spectrum of dark-web users. Its inventory primarily includes:
- Privacy-focused digital goods: Encrypted communication tools, VPN subscriptions, and secure cloud storage.
- Cryptocurrency and financial services: Crypto mixers, anonymous cryptocurrency exchanges, prepaid virtual cards, and financial accounts.
- Digital and counterfeit items: Documents such as passports, IDs, licenses, and educational diplomas.
- Pharmaceuticals and controlled substances: Primarily pharmaceuticals, cannabis, psychedelics, and select stimulants—strictly regulated within internal marketplace guidelines.
Notably, Abacus explicitly forbids highly dangerous goods, including weapons, explosives, and exploitative material, which has helped maintain a relatively favorable reputation among its user base.
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
- Advanced Security: Utilizes end-to-end encrypted communication, mandatory PGP verification for vendor interactions, and multi-signature escrow wallets, significantly reducing risks of scams.
- Reliable Escrow System: Features automated escrow and dispute resolution through smart contracts, boosting user confidence.
- Strong Vendor Management: Strict vendor verification processes and transparent feedback mechanisms ensure marketplace trustworthiness and consistency.
Weaknesses:
- Occasional Downtime: Due to frequent security audits and infrastructure updates, users occasionally experience temporary downtime.
- Limited Product Scope: While its strict moderation policy enhances its ethical reputation, some users perceive the absence of certain product categories as restrictive.
Security and Anonymity Features
Abacus Market employs several robust security measures to ensure user anonymity and safety:
- Tor and I2P Integration: Users can access Abacus through either the Tor or I2P networks, providing flexibility and strong anonymity protection.
- Mandatory Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Every user is required to enable 2FA, significantly reducing unauthorized account access risks.
- Monero Integration: Primarily accepts Monero transactions, enhancing transactional privacy and obscuring users’ payment trails.
- Built-In PGP Encryption: Vendor communication and order details are fully encrypted through built-in PGP tools, further securing sensitive information.
Overall, Abacus Market distinguishes itself through rigorous security measures, effective moderation policies, and a strong emphasis on protecting user privacy. Despite minor accessibility inconveniences, these strengths have solidified its position among the top dark-web marketplaces in 2025.
DarkMatter Market
DarkMatter Market is portrayed in open‑source threat‑intel as a privacy‑first marketplace that went live in September 2022. Trackers emphasize its Monero‑only policy and a walletless payment design intended to minimize on‑site custodial balances. As of 2023, Searchlight Cyber estimated roughly 6,000 listings and ~300 vendors, and attributes admin handles such as “quasar1,” “BlackMask,” and “zamman.” Treat those figures as directional; hidden‑service data shifts quickly.
Inventory & Positioning
Public monitoring describes DarkMatter as primarily drug‑centric, with additional categories reported for fraud, counterfeit documents, and malware/digital tools—a mix consistent with mainstream DNMs. The project’s marketing leans heavily on “security/education” messaging, aligning with its privacy‑coin‑only stance. Specific moderation rules are not authoritatively documented on clearnet sources and can change over time.
What Stands Out (as reported)
-
Monero‑only & walletless flow: OSINT profiles highlight XMR‑only settlement and walletless ordering (no custodial market balance), framed as a defense against exit‑scam concerns.
-
Escrow and multisig, per trackers: Community directories and “review” sites claim escrow with XMR multisig (2‑of‑3) support. Treat these as third‑party claims unless independently verified.
-
“Accountless” ordering is advertised in some places: A few promotional pages suggest guest‑style purchases; again, regard this as marketing copy rather than a verifiable guarantee.
Trade‑offs & Ecosystem Risks
-
Information asymmetry: Much of what’s known about DarkMatter comes from trackers and promotional pages, which can lag reality or contain hype. Use with caution.
-
Sector volatility: 2024–2025 continued to see major disruptions—global operations like Operation RapTor and high‑profile market exits (e.g., Abacus’s likely exit scam) illustrate the constant enforcement and stability pressure all DNMs operate under.
-
Payment privacy ≠ risk elimination: Chainalysis notes a broader trend toward Monero‑only acceptance among Western DNMs as BTC’s traceability raises exposure—useful context for DarkMatter’s design, but not a safety assurance.
Security & Privacy Model (as described publicly)
-
Network & access: Tor hidden service; no clearnet operational details are cited here. (General characterization from OSINT profiles.)
-
Payments: XMR‑only, with walletless architecture reported by Searchlight Cyber; some directories additionally claim XMR multisig escrow.
-
Marketplace mechanics: Standard escrow and reputation/feedback are described across trackers; specifics can vary and are often self‑reported.
DarkMatter Market is framed by open sources as a privacy‑forward, Monero‑only marketplace that leans into walletless flows and (reportedly) XMR multisig—choices that fit the post‑2022 shift toward harder‑to‑trace settlement. Those design decisions don’t remove structural risks: ecosystem volatility, phishing/DDoS, and sustained law‑enforcement pressure remain defining features, and public details can change without notice.
Apocalypse Market
Open‑source datasets place Apocalypse Market among the wave of “second‑generation” DNMs that appeared in late 2022 (first observed sales on December 16, 2022). It was listed as active through the end of 2023 in the EU Drugs Agency (EUDA) marketplace dataset; community trackers later labeled the site closed—a reminder that hidden‑service status can flip quickly. EUDA+1
Inventory & Positioning
Public OSINT and market trackers describe Apocalypse as a general‑purpose marketplace with the usual vendor‑driven mix—drugs & chemicals, fraud/financial items, counterfeit documents, software/malware/tools, and guides—consistent with category patterns documented across DNMs. Treat category rosters and counts from tracker pages as indicative, not definitive.
What Stood Out (as reported)
-
Standard trust mechanics. Trackers describe escrow and reputation/feedback flows typical of modern DNMs; some posts mention vendor bonds/fees for new sellers (amounts vary by source). These features aim to curb straightforward fraud but never eliminate risk.
-
Low barrier to vend (claimed). A frequently cited LinkedIn post asserted that anyone could buy a vendor account for ~$250; treat this as a third‑party claim rather than an audited policy.
-
Operational turbulence. Community write‑ups allege at least one security misstep (an IP‑leak incident attributed to admin error) in 2023; that specific episode is reported in community blogs and OSINT roundups, not in primary law‑enforcement disclosures.
Trade‑offs & Ecosystem Risks
-
Volatility is the norm. Even well‑run DNMs face DDoS, phishing/impersonation, and abrupt shutdowns or seizures. 2024–2025 saw continued, highly visible enforcement actions (e.g., June 2025’s Archetyp takedown), which reshape traffic and trust across the ecosystem—Apocalypse included.
-
Escrow ≠ safety. Academic work on DNM “security advice” notes that escrow protects buyers in some cases but also concentrates trust in admins—no marketplace mechanism is a guarantee.
-
Tracker bias. Much of what’s known about Apocalypse’s features (coins, bonds, listing counts) comes from community directories that can lag reality or contain marketing embellishments. Use OSINT claims as directional context.
Security & Privacy Model (as described publicly)
-
Network & access: Tor hidden service; status fluctuated by 2025 per public trackers.
-
Account & comms: Typical PGP‑centric buyer–vendor messaging with reputation/feedback. (General DNM model; site‑specific docs are scarce on the clearnet.)
-
Transactions: Escrow‑based settlement reported by trackers; some mention vendor bond/fee requirements for new sellers.
-
Currencies: Trackers state cryptocurrency settlement (commonly BTC and/or XMR on peer markets), but coin menus change and are inconsistently reported in public write‑ups.
Apocalypse Market is portrayed in OSINT sources as a late‑2022, general‑purpose DNM that adopted the familiar escrow + reputation playbook and (reportedly) vendor bonds/fees—with at least one notable opsec stumble circulating in community accounts. As of September 2025, public trackers mark it closed, underscoring the sector’s churn amid phishing/DDoS and sustained law‑enforcement pressure.
Flugsvamp 4.0
Flugsvamp 4.0 (FS4) launched on November 2, 2021 as the successor to Sweden’s domestic‑shipping cryptomarket Flugsvamp 3.0, which its administrators had taken offline on October 30–31, 2021. Academic work tracking the Swedish scene notes that FS4 never matched its predecessor’s traction; instead, a critical mass of Swedish vendors migrated to the German‑run Archetyp Market, citing trust and usability concerns around FS4 (including community rumors of fraud and early technical hiccups).
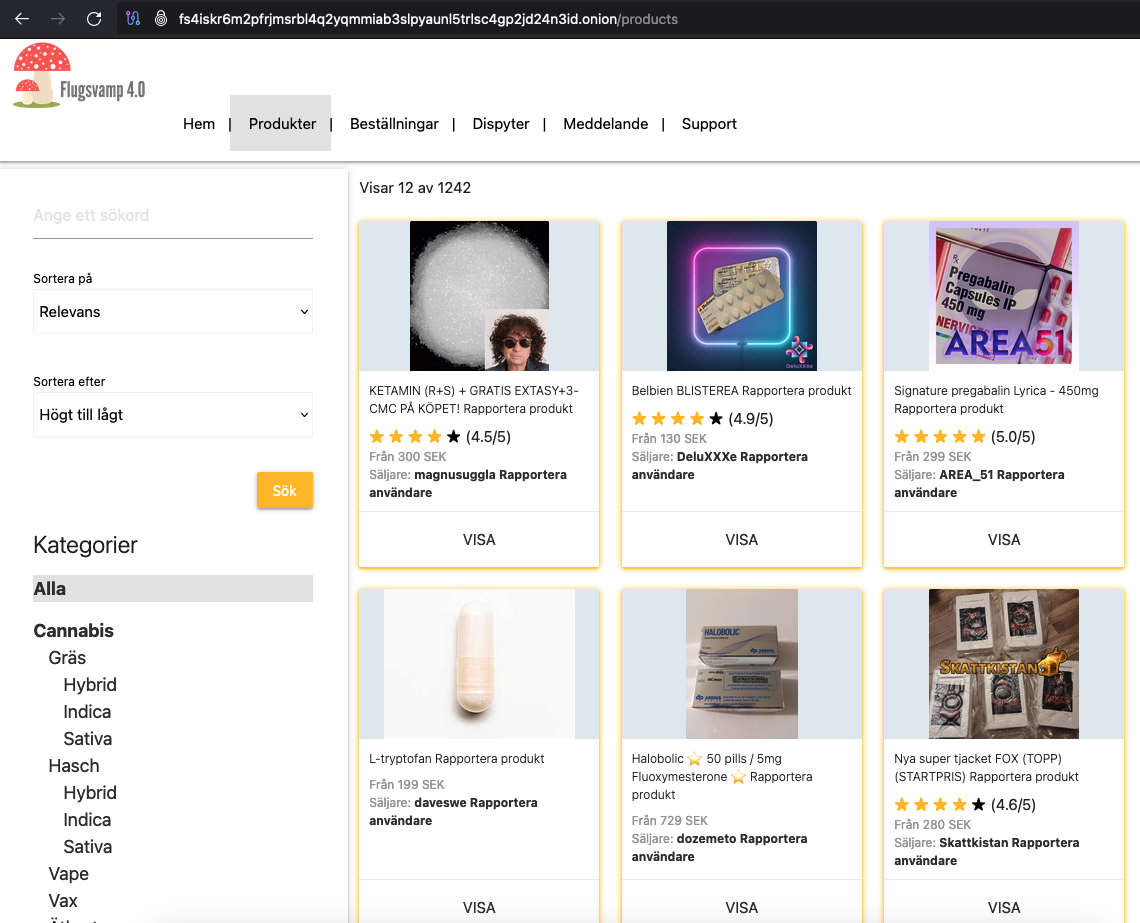
Market Scope & Positioning
FS4 has been described as a Sweden‑centric, drug‑led marketplace that follows the broader European DNM pattern: regionally oriented shipping, vendor‑run storefronts, and category mix dominated by narcotics with some digital/fraud listings. This aligns with longer‑run research showing drugs make up the bulk of cryptomarket trade and that Scandinavian markets often emphasize domestic parcels to avoid cross‑border risk. Europol+1
What Stood Out (as reported in open sources)
-
Post‑closure fragmentation: After FS3 went dark, many Swedish vendors rejected FS4 and set up on Archetyp, shaping Swedish buyer traffic in 2022–2024. That migration dynamic is well‑documented in peer‑reviewed work.
-
Conflicting payment claims: Third‑party directories disagree on FS4’s coin support—some list BTC‑only deposits, others add Monero and even XMR multisig escrow. Treat these as unverified tracker claims rather than audited facts.
-
Standard trust mechanics (reported): Trackers describe escrow, reputation/feedback, and PGP‑centric messaging—typical for contemporary DNMs. As with coin menus, these descriptions are OSINT‑based and can lag reality.
Strengths & Trade‑offs
Strengths
-
Regional identity: Swedish‑language community and domestic‑shipping focus can reduce customs exposure and build a tight buyer–seller network—advantages commonly cited for regional markets.
-
Familiar UX for DNM users: Even critics describe FS4’s model as the standard “vendor listings + escrow + feedback,” which lowers switching costs for returning users.
Trade‑offs
-
Adoption headwinds: FS4 struggled to regain FS3’s network effects; vendor displacement to Archetyp depressed liquidity, and Archetyp’s June 2025 takedown later re‑shuffled the ecosystem again.
-
Information asymmetry: Much of what’s publicly known about FS4’s features (coins, escrow flavor, anti‑phishing steps) comes from community directories and can be out of date or promotional. Cross‑checking is essential.
-
Ongoing enforcement pressure in Sweden: Prosecutions tied to FS3 (including an April–July 2024 sentencing of the operator to nearly 12 years) show sustained national focus, which shapes user trust and migration across Swedish‑facing markets. Drugnews
Security & Privacy Posture (as described)
-
Access & comms: Tor hidden‑service access; trackers describe PGP‑based buyer–seller messaging and reputation systems. Consider these claims indicative, not definitive.
-
Transactions: Reports consistently mention escrow; details such as multisig and exact coin support vary by source.
Flugsvamp 4.0 presents as a localized, drug‑centric market that inherited the Flugsvamp brand but not its full network effects. Scholarly analyses highlight how Swedish vendors largely migrated away from FS4 after 2021, with the 2025 Archetyp takedown again reshaping where Swedish traffic lands. As with any hidden service, features and status are fluid; third‑party tracker details should be treated as directional rather than definitive.
Ares Market
Ares Market is commonly profiled by threat‑intel trackers as a general‑purpose dark‑web marketplace that appeared in 2021. Open‑source snapshots describe a broad vendor mix spanning drugs, fraud/financial items, counterfeits, and digital tools—the standard DNM catalog. These roundups stress that listing volumes and category prominence fluctuate over time.
Positioning and Feature Claims (as described publicly)
Clearnet “directory” pages and market overviews frequently characterize Ares as using a walletless / direct‑pay approach with escrow, plus support for BTC and XMR (sometimes listing additional coins). They also tout PGP‑based messaging and 2FA at the account level. Treat these as self‑reported marketing details rather than independently verified features; such pages are useful for understanding how the site portrays itself but can lag reality.
What Trackers Emphasize About Inventory
Analyst write‑ups point to a wide spectrum of vendor‑run listings, with drugs typically dominant and fraud/digital‑goods categories active. These summaries echo the familiar “escrow + vendor reputation” model—reviews and sales history as primary trust signals. Because hidden services evolve quickly, product counts and mix should be read as indicative, not definitive.
Security & Privacy Model (sector context)
Independent research on DNMs documents recurring security mechanisms across markets: onion‑only access, anti‑phishing measures and CAPTCHAs, PGP for buyer–seller comms, MFA/2FA, and financial‑layer controls like escrow and sometimes multisig. Ares is commonly described in that mold; still, specific implementations and coin menus vary and are rarely authoritative on the clearnet.
Frictions and Structural Risks
-
Ecosystem volatility. 2024–2025 brought sustained disruption (takedowns, exits, DDoS, phishing). Europol’s June 16, 2025 operation against Archetyp Market is a recent example of coordinated enforcement that reshapes user trust and traffic across DNMs. Europol
-
Revenue and coin‑use trends. Chainalysis reports that on‑chain BTC inflows to DNMs fell amid years‑long enforcement pressure, while many Western markets lean into privacy‑coin acceptance—useful macro context for sites that advertise Monero support.
-
Information asymmetry. High‑level, official datasets (e.g., EUDA’s) show how market status changes rapidly and that public tables are checked at specific cutoffs (e.g., Dec 31, 2023). Treat any clearnet “feature list” or “active mirror” page as provisional. EUDA
Bottom Line
Ares Market is presented in open sources as a general‑purpose marketplace with a familiar trust stack (escrow, feedback, PGP/MFA) and BTC/XMR settlement—features that align with sector norms rather than set it apart. As with any hidden service, availability, policies, and coin options can change without notice; much of what’s known is either a point‑in‑time analyst snapshot or self‑reported market copy.
Typical Use-Cases of Dark-Web Marketplaces in 2026
Dark-web marketplaces often attract attention due to their association with illicit activities; however, these platforms also serve legitimate purposes that align closely with principles of online privacy and freedom of information. Understanding both the lawful and unlawful scenarios helps provide a balanced view of their practical applications in 2025.
Legitimate Use-Cases
- Investigative Journalism:
Journalists and whistleblowers frequently use dark-web platforms to share information securely and anonymously. These marketplaces can provide crucial access to encrypted communication tools, secure storage services, and data protection software, enabling sensitive investigations into corporate wrongdoing, government corruption, and human rights violations without compromising the identity of sources. - Cybersecurity Research:
Security professionals and researchers utilize dark-web marketplaces to monitor emerging cyber threats, malware trends, and stolen data marketplaces. By studying these environments, cybersecurity experts gain insights into hacker methodologies and vulnerabilities actively exploited in the wild, enabling proactive defense strategies to protect individuals, businesses, and critical infrastructure. - Protecting Privacy in Restrictive Environments:
Individuals living under oppressive governments or facing severe censorship often turn to the dark web to access privacy-enhancing tools like VPNs, encrypted messaging apps, and anonymizing services. Dark-web marketplaces provide essential resources to activists, dissidents, and ordinary citizens who rely on anonymity to safely express opinions, share information, and communicate without surveillance or persecution.
Illicit and Risky Use-Cases
- Illegal Trade of Controlled Substances and Goods:
Many dark-web marketplaces facilitate illegal transactions involving controlled substances, pharmaceuticals, counterfeit goods, and unauthorized items. Despite efforts by law enforcement, platforms continue to provide anonymous channels for buyers and sellers to trade substances that would otherwise carry substantial legal penalties and health risks. - Data Breaches and Identity Fraud:
Stolen personal and financial data—such as login credentials, Social Security numbers, and credit card information—frequently appear for sale in these marketplaces. Cybercriminals monetize data breaches by trading vast datasets, which other malicious actors use for identity theft, financial fraud, and sophisticated social engineering attacks. - Financial Fraud and Cybercrime Tools:
Specialized marketplaces offer various cybercrime-as-a-service options, including ransomware toolkits, phishing services, and financial fraud instruments such as fake documents, cloned payment cards, and banking malware. These illicit offerings significantly contribute to the ongoing challenge of cybercrime globally.
Understanding these contrasting use-cases underscores the complex role dark-web marketplaces play in contemporary digital society, serving both legitimate needs and presenting significant challenges for security and law enforcement agencies worldwide.
Primary Risks and Dangers of Using Dark-Web Marketplaces
Engaging with dark-web marketplaces comes with substantial risks that users should understand clearly before proceeding. Although platforms promise anonymity and security, vulnerabilities persist, potentially leading to severe consequences. Below are the primary dangers users may encounter:
Legal Consequences
Activities on dark-web marketplaces are closely monitored by international law enforcement agencies. Purchasing or selling illegal goods—such as controlled substances, counterfeit documents, or stolen data—can result in significant legal penalties, including fines, criminal charges, and imprisonment. Even users who access these platforms without intent to buy illegal items risk suspicion or investigation.
Cyber-Attacks and Scams
Dark-web marketplaces attract sophisticated cybercriminals adept at launching phishing scams, malware attacks, or ransomware threats. Buyers and sellers frequently face risks from malicious actors posing as legitimate vendors or customers, potentially leading to financial loss or exposure of sensitive personal information.
Loss of Anonymity
Although dark-web marketplaces utilize technologies like Tor and I2P to enhance anonymity, these methods are not foolproof. Law enforcement agencies continuously improve their ability to trace transactions and monitor marketplace activity. Simple mistakes—such as inadequate operational security practices, sharing identifiable details, or using compromised devices—can quickly compromise anonymity and expose users’ real-world identities.
Cryptocurrency-Related Vulnerabilities
Cryptocurrencies, while offering enhanced privacy, also present significant risks. Users face vulnerabilities like market volatility, scams involving fake escrow services, compromised wallets, or theft through phishing schemes targeting crypto transactions. Furthermore, inexperienced users unfamiliar with secure cryptocurrency practices are particularly susceptible to these threats, risking the loss of their entire funds.
Overall, dark-web marketplaces inherently involve substantial risk, and users must thoroughly understand these threats. Anyone considering engaging with these platforms must carefully evaluate potential consequences, exercise stringent security practices, and remain vigilant to minimize exposure to these significant hazards.
Essential Security Tips for Using Dark-Web Marketplaces
Navigating dark-web marketplaces requires rigorous precautions to protect your identity, financial assets, and ensure you remain within legal boundaries. Below are essential practices every user should follow:
1. Maintain Your Anonymity
- Use Tor or I2P: Always access marketplaces exclusively via secure, anonymizing networks such as the Tor Browser or I2P network to mask your IP address and location.
- Leverage VPNs: Employ a trusted VPN service in combination with Tor to add an extra encryption layer, further protecting your browsing activity.
- Consider Tails OS: Run the privacy-focused operating system Tails from a USB stick or virtual environment. Tails routes all internet traffic through Tor and leaves no trace of your activity on the device you use.
2. Secure Your Cryptocurrency Transactions
- Use Privacy-Oriented Cryptocurrencies: Prioritize currencies like Monero, which conceal transaction details more effectively than Bitcoin.
- Hardware Wallets and Cold Storage: Store your cryptocurrency securely in hardware wallets or cold storage solutions to avoid theft or unauthorized access.
- Verify Escrow and Vendor Reputation: Always transact through verified escrow services provided by trusted marketplaces and thoroughly review vendor reputations before making purchases.
3. Stay Within Legal Boundaries
- Know Your Jurisdiction: Familiarize yourself thoroughly with the laws and regulations applicable in your jurisdiction regarding dark-web activities and the products or services you access.
- Avoid Illegal Transactions: Refrain from purchasing or engaging with prohibited products and services. Law enforcement agencies actively monitor marketplaces, and illegal activities significantly increase your risk of detection and prosecution.
- Practice Strict Operational Security (OpSec): Never share personal, identifiable information, and avoid using the same usernames, passwords, or cryptocurrency addresses across multiple platforms.
By consistently applying these straightforward security tips, you can significantly mitigate risks and better protect your privacy, finances, and legal standing when interacting with dark-web marketplaces.
Future Trends and Predictions for Dark-Web Marketplaces Beyond 2025
Looking ahead, dark-web marketplaces will continue to evolve rapidly, shaped by emerging technologies, shifting regulatory landscapes, and changing user behaviors. Here are key trends and predictions likely to influence these platforms in the coming years:
Technological Advancements
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration:
AI technologies will increasingly manage dark-web marketplace operations, enhancing security measures, vendor reputation systems, and dispute resolution. Automated AI-driven escrow systems will detect fraud attempts earlier and with greater precision, improving overall trust among marketplace participants. - Quantum Computing and Cryptography:
The advent of quantum computing poses a major threat to traditional encryption methods. In response, dark-web marketplaces will adopt quantum-resistant cryptography to maintain security and user anonymity. Early adopters of quantum-safe algorithms will likely gain significant advantages over slower-moving platforms. - Enhanced Blockchain Integration:
Blockchain technology, particularly decentralized finance (DeFi) and smart contracts, will become central to transactions on dark-web marketplaces. These innovations will improve transaction transparency, reduce fraud risk, and provide enhanced privacy through decentralized and anonymized financial services.
Regulatory Changes and Enforcement Strategies
- International Cooperation and Legislation:
Law enforcement and regulatory agencies will strengthen global cooperation, leading to more coordinated marketplace takedowns and increased prosecutions. Expect stricter international laws targeting anonymizing technologies, cryptocurrencies, and digital exchanges that facilitate illicit dark-web activities. - Expanded Surveillance and Monitoring:
Advanced tracking tools and monitoring techniques, including blockchain analytics, machine learning-driven traffic analysis, and quantum-enhanced surveillance methods, will challenge traditional anonymity measures, pushing dark-web users toward ever more sophisticated privacy protections.
Shifts in User Behavior and Marketplace Structures
- Rise of Decentralized Marketplaces:
Centralized platforms will decline in favor of decentralized, peer-to-peer marketplaces resistant to law enforcement disruption. Decentralization reduces vulnerability to single points of failure, significantly enhancing marketplace resilience and longevity. - Increased Ethical and Privacy-Conscious Use:
A growing number of users will seek dark-web marketplaces for legitimate reasons—privacy protection, secure communication, and bypassing censorship rather than illicit activities. Marketplaces catering specifically to ethical, privacy-conscious consumers will likely expand, reshaping public perceptions of the dark web.
In summary, beyond 2025, dark-web marketplaces will increasingly blend cutting-edge technologies with adaptive strategies to survive in an environment marked by heightened regulatory oversight and shifting user priorities. Users and cybersecurity professionals alike must stay informed and prepared to navigate this rapidly changing digital frontier.
Conclusion
In exploring the top 11 dark-web marketplaces in 2026, we’ve examined their core operations, diverse use-cases, inherent risks, and evolving trends. While these marketplaces continue to serve legitimate purposes, such as enabling secure communication and privacy protection, they also remain hotspots for illicit activities and cybercrime. Technological advancements like AI-driven security, quantum-resistant encryption, and blockchain integration are reshaping the landscape, but simultaneously, global enforcement efforts grow more sophisticated and collaborative.
As a user or cybersecurity professional, approaching these marketplaces demands utmost caution, thorough knowledge of operational security, and constant awareness of legal boundaries. Understanding both the benefits and dangers ensures safer interaction and more informed decision-making in an ever-changing digital environment.